 Book Appointment
Book Appointment
 +91 77740 40002
+91 77740 40002
Cervical Laminoplasty Treatment is a surgical procedure to widen the space available for the cervical spinal cord. It is a useful procedure for patients with compressive cervical myelopathy wherein the spinal cord gets squeezed due to the degenerative changes in the cervical spine.
Cervical Laminoplasty Treatment Procedure involves the use of plates and screws to widen the space for the spinal cord. Lamina is section of bone that cause a roof over the spinal canal. In the procedure, a hinge is created on one side of the lamina, and the other side is wedged to open by a small metallic plate or a bone strut.
Laminoplasty is generally performed in the neck on cervical spine. Also, it may be performed in the middle or low back on thoracic or lumbar spine, especially in pediatric or younger adult patients. The procedure is sometimes performed to treat compression or the pressue on spincal nerves or spinal chord, which is caused by narrowing spinal canal. Laminoplasty a type of decompression surgey. Compression on the spinal nerves can produce pain, weakness, or numbness in a single arm or hand. Compression on the spinal cord can cause serious problems. It can permanently damage the delicate tissues of the spinal cord. Myelopathy, that is spinal cord compression may produce weakness, or numbness in both arms or legs, difficulty walking, or bladder control or impaired bowel.
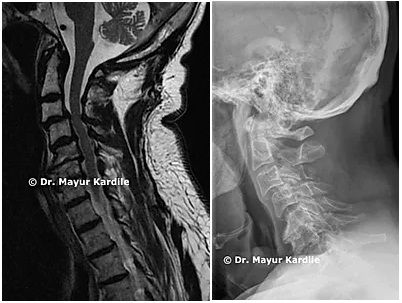
Decompression with Cervical Laminoplasty can treat conditions such as:
1.Cervical Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal in the cervical spine
2.Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: degenerative changes that cause myelopathy in the cervical spine Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: A condition in which a ligament in the spinal canal becomes thickened and inflexible
it keeps the normal bone and ligament structure intact as compared to laminectomy which removes the lamina instead of hinging it open.
It helps to keep spinal balance normal, especially in the patients with spinal degeneration.
It also provides a protective layer that prevents scar tissue formation on the nerve (dural) sac after surgery.
It is a useful treatment option in some pediatric patients, since they are at greater risk than adults for spinal instability following the more extensive bone removal in a laminectomy.
For, individuals who need a greater amount of decompression may be more effectively treated with the full removal of the lamina, a laminectomy, since laminoplasty provides lesser decompression.
When deciding on the best treatment, surgeons take into account a variety of factors, including the patient's age and medical status, spinal curvature, spinal column mobility as determined by flexion/extension X-rays, the number of spinal segments involved, the position of the main component of spinal cord compression (in front of or behind the spinal cord), and the degree of calcification of bone spurs. Patients with two or more degrees of spinal stenosis, normal cervical curvature or a straight cervical spine, no repetitive motion on flexion/extension X-rays, and minimal or no neck pain are the best candidates for cervical laminoplasty.
This surgical procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The back of the spinal column is visible after an incision is made down the middle of the back of the neck.
The surgeon makes a thin cut in the bone at the junction of the lamina and a spinal joint called the facet joint, using an operating microscope and very fine surgical instruments.This cut goes all the way into the bone's outer and middle layers. A similar cut is made on the opposite side of the bone, going through the outer, lower, and inner layers of the bone.The lamina is wedged open after both cuts are made, instantly opening up the spinal canal and relieving pressure on the spinal cord.
During a laminoplasty, the surgeon may also perform a foraminotomy. This procedure enlarges the foramina, the holes through which nerve roots exit the spinal cord. A foraminotomy is a procedure that can soothe pressure on nerve roots.
The surgeon will then close the incision and dress it with a bandage.
Make sure your doctor is aware of any drugs you're taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements, especially blood-thinning medications like aspirin. Before your procedure, your doctor may advise you to stop taking these medications. To make it even simpler, jot down all your medicines before the surgery.
If you're allergic to any drugs, foods, or latex, make sure to tell your doctor (some surgical gloves are made of latex).
Remove any nail paints or acrylic nails as well as any makeup and jewellery before your surgery.Carry any necessary things, such as a toothbrush, toothpaste, and dentures, if staying overnight.
Any surgical procedure is like an injury. After a cervical laminoplasty treatment, there will be some discomfort and limitation of motion for a few weeks. You will probably stay in the hospital for one to two days, and you may need some pain medication for a short period of time. Your activity may be limited for a few weeks. You may increase your level of activity as you feel comfortable. Activities such as driving and returning to work depend on your own personal comfort and safety level.
The surgeon will schedule a follow up visit, typically 4-6 weeks after surgery. At this time, the surgeon will check healing, range of motion, the balance of the spine, and any other symptoms.